Otto M. Machado Filho and Nelson F. F. Ebecken
NPPG / DCC / POLI / Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil
ABSTRACT
Knowledge retrieval has been recognized as a key issue in engineering design projects. A great amount of design information is generated during design verification steps. Engineering documents are generally verified using checklists. These checklists have a long list of items which need to be checked against the document being reviewed. The engineer or designer needs to check each item on the checklist in order to determine whether the document is suitable for approval.
Checklist records can become more useful if they generate a database which can be retrieved and used in forecasting models, enabling avoidance of future design mistakes. These forecasting models aim to enhance the projects performance by reducing future corrective actions, which are time-consuming and costly.
The objective of this paper is to improve the performance of engineering projects by reducing design corrections with the help of an expert system. This expert system’s role is to capture the expert’s knowledge, design information and data from the verification checklists; and then, process the collected data in order to anticipate potential design projects mistakes. In addition, this expert system has been validated with an engineering design project company.
Keywords: Expert System; Knowledge Database; Engineering Design Projects; Forecasting Model.
1. INTRODUCTION
The need to compress project schedules has put pressure on traditional engineering projects. It is clear that there is still a need for innovative research in the area of engineering design projects.
Design verification represents an essential step in engineering design projects. The verification purpose is to ensure that all design tasks are completed in accordance with the specifications or are carried out in accordance with appropriate standards and methods.
Once documents are verified through electronic checklists, a computer system is able to use the database to provide information that improves design project performance.
This paper proposes an innovative expert system to capture data from the electronic checklists and then, use the expert knowledge to process the collected data in order to anticipate potential design projects mistakes. The approach demonstrates to be efficient in terms of reducing time and cost of engineering design projects once it increases the document elaboration accuracy and decreases man-hour used in verification and revision steps.
Literature on similar subject, i.e., engineering design error prediction is unknown. Thus, this work can be considered extremely innovative.
The remaining parts of this paper are organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the methodology. Section 3 presents the implementation. The results are discussed in Section 4. Finally, Section 5 draws some conclusions.
2. METHODOLOGY
An Expert System [2, 4] is a problem solving and decision making system based on logical rules and historic database. These expert systems represent the expertise knowledge as data and rules which can be called to solve problems.
In this paper, the expert system roles have been designed to capture the knowledge of the experts and the data of engineering design checklists. After that the system is able to process these data and form rules to present alert with potential design errors. Figure 1 illustrates the system model.
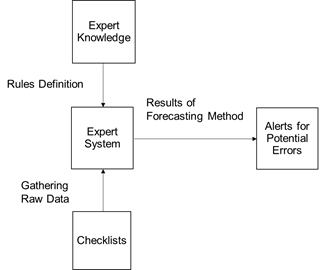
There are two main parts to the expert system: gathering the raw data and rules definition.
2.1. Gathering the Raw Data
Design documents in engineering projects passes through a standard workflow composed by activities executed in a certain order with one professional responsible for each step, beginning with execution/design, following to verification and revision and concluding with document’s issuing, as demonstrated in Figure 2.
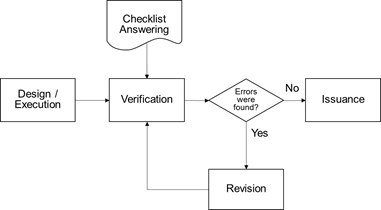
When the document reaches the verification stage, a senior engineer or designer will verify that document using a verification checklist, an auxiliary tool composed by several questions that need to be attended according to appropriate standards, methods and client’s specifications.
As the verification stage finishes and all questions are answered, the professional will advance the design to the next activity or, in case of required corrections, document will be returned to revision stage, where another professional will correct errors found. This process can be redone as many times as necessary, until the document has no more errors, being known as verification cycle.
As checklists are filled, the expert system creates a database with complete information about what is being answered on those checklists, compiling all data such as total errors by discipline, document type and professionals profile. With all this data at disposal, the system can now analyze the patterns and tendencies, tracing parameters for detection of potential future errors.
2.2. Rules Definition
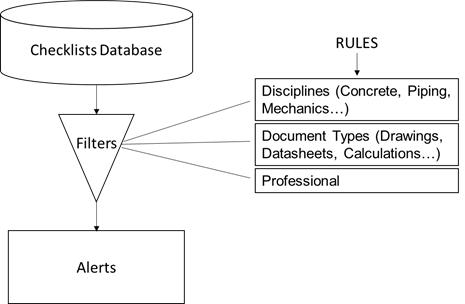
While analyzing the data acquired, the expert system will create a ranking of the most common errors ordered by professional profiles and documents characteristics; then will apply conditional rules to define the alert for each user about the most probable design errors.
In the first moment the system will try to select most frequent errors for the specific professional and document features, as showed in Figure 3. Although, if there are no representative checklist records in the database for this filter, the system will reduce the constraints, considering errors for similar professional profile and document characteristics.
After the data selection, the system shows an alert box, containing most probable errors, advising the user to be careful about these mistakes while designing the document.
3. IMPLEMENTATION
In this work, the expert system was implemented inside an electronic document management system (EDMS) [3], called SAPROD [5], currently being used by design engineering companies. EDMS is a type of software that electronically manages the document lifecycle. It enables a detailed control of documents workflow and provides indicators related to process quality and professional productivity.
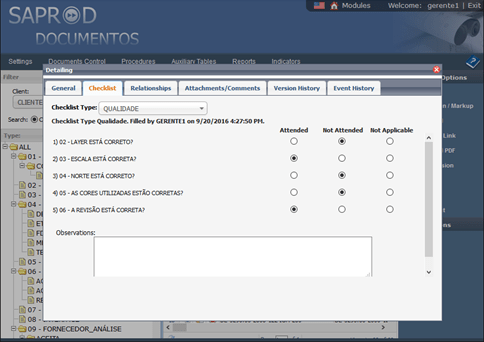
As the designer concludes the design elaboration, the document will proceed to the verification stage through the system workflow. The person responsible for design verification must fill up the electronic checklist, embedded in the system, in order to proceed to the next stage, as showed in Figure 4.
After checklist errors database creation, new alerts will be displayed, before elaboration stage is started, as presented in Figure 5. The alerts show most probable errors, based on professional profile and document characteristic. Through this alerts, system helps to prevent similar errors in the project.
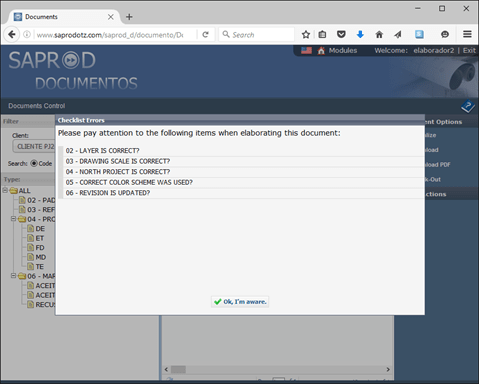
The designer must to confirm the alert information, by clicking in a button “Ok, I’m aware”. The confirmation is stored in the system for future consulting.
4. RESULTS
The proposed approach has been tested in a real scenario. A design engineering company that uses the software SAPROD, allowed a study involving two very similar projects undergoing simultaneously. The expert system has been used in one project to predict the design errors while the other project followed the standard process. This analysis allowed an effective demonstration of the methodology results.
When comparing both projects performance, it has been verified that the project with error forecasting methodology had a reduction of 16% in percentage of checklist items with error. It has been considered only the checklists filled in the first verification cycle for each design document, i.e., it has not been considered the checklists filled after the document revisions.
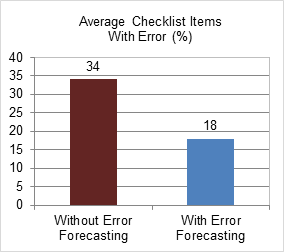
Figure 6. Average Checklist Items With Error
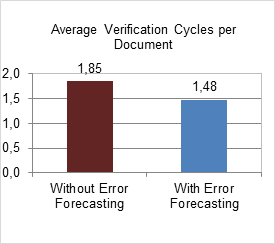
Another indicator is related to the reduction of verification cycles. Project with error forecasting method had a decrease of 20% in average of verification cycles per document, as presented in Figure 7.
As less workhours were spent in verification and revising stages, it has been verified a reduction of approximately 6,4% in the design project cost and duration.
5. CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, an expert system is presented to manage verification checklist database in order to anticipate potential design errors, before the design elaboration.
Expert Systems are artificial intelligence [1, 6] tools that apply the expertise of knowledge workers in a database and provide advice to non-experts in a given domain.
The methodology has been implemented in a commercial electronic document management system (EDMS), called SAPROD, which control documents workflow and enable electronic checklists for document verification stage. Once the checklists are recorded in system database, expert rules are used to select the most frequent error for each professional profile and document feature, showing alerts to the designer before the document beginning.
A case study was analyzed to illustrate the benefits of the developed method. The results confirmed a reduction of cost and time for engineering design project that considerer the proposed approach.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- Dean, T., Allen, J., and Aloimonos, Y., 1995, Artificial Intelligence: Theory and Practice. Redwood City, CA: Benjamin/Cummings.
- Durkin, J., 1993, Expert Systems: Catalog of Applications, Akron, OH: Intelligent Computer Systems.
- Koulopoulos, T. M. and Frappaolo, C., 1994, Electronic Document Management Systems: A Portable Consultant, McGraw-Hill Book Company.
- Mockler, R.J. and Dologite, D.G., 1992, Knowledge-Based Systems: An Introduction to Expert Systems. New York, NY: MacMillan.
- Online Available: http://www.saprod.com.br/en/homepage-2/.
- Russell, S.J. and Norvig, P., 1995, Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.